本文汇编代码可参见:
操作结构体
上文提到C语言中只提供了两种基本的数据操作方式:列表和结构体。列表是同类数据的连续排列,结构体则是不同种数据类型的汇集。
基于以上两种数据操作方式我们便可以实现各种复杂的数据结构了。由于取结构体元素的操作大致都基于偏移量实现,而且计算均由编译器完成,所以在此我们无法像上文一样给出类似的库函数去做同一操作。具体可见下面的例子。
struct Temp {
int a;
int b;
int c;
} temp;
temp.b = 1;
的C语言功能可由下述汇编实现(假设寄存器a0保存了temp的地址)
li t0, 1
sw t0, 4(a0)
结构体的成员类型都是整形,占4字节。所以成员b关于该结构体头部地址的偏移量即为4,则可由sw命令直接存入。
可见结构体的操作极其依存于其具体实现,在本文中我们将以顺序表为例,实际操作一下结构体。
顺序表
关于顺序表的详细定义我们在此跳过,直接步入具体实现。
这里我们采取分离式结构,即
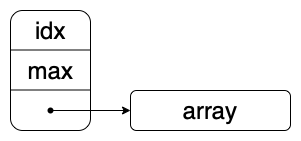
在所有存取、修改过程中通过维护当前可存入下标idx的方式确保正确操作。上述结构可以按照如下的C语言结构体理解。
typedef struct slist {
int idx;
int max;
int* array;
} Slist;
创建
# make list
# parameters
# a0 = length(in words)
# returns
# a0 = address
make_slist:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -8
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw a0, 4(sp) # store len
# slist struct (len + max + addr of list)
li a0, 3
call malloc
sw zero, 0(a0) # set len
lw t0, 4(sp) # t0 = max len
sw t0, 4(a0) # set max len
# allocate list
sw a0, 4(sp) # store slist
lw a0, 4(a0) # a0 = max len
call malloc # a0 = addr of list
lw a1, 4(sp) # a1 = slist
sw a0, 8(a1) # set addr of list
mv a0, a1 # a0 = slist
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 8
ret
在创建过程中由于采用了分离式结构,第三成员保存的是实际存储列表的地址(指针),所以需要进行两次内存分配操作。为确保函数调用间的寄存器数据安全,我们将重要且会复用的数据暂时退避到栈内。在设定好一切必要成员信息后将头部地址返回。
这样一来我们便可以通过idx来判断该顺序表是否为空了。此操作时间复杂度为$O(1)$。
# is empty
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# returns
# a0 = bool
slist_is_empty:
lw a0, 0(a0) # a0 = len
slti a0, a0, 1 # a0 = (a0 < 1) ? 1 : 0
ret
末尾插值/删除
得益于前面定义的结构,使顺序表的尾端操作变得十分简单。由于不涉及既有元素的移动,我们只需要调整idx部分的数值即可(idx部分既代表当前的可插值位置,同时也等同于当前的表长)。因此这两种操作的时间复杂度为$O(1)$
于是对于末尾加值,将新值存入当前idx位置后,增加一个表长即可。此外,为了确保操作的安全性,我们最好在插入前检查一下当前的表是否已满。
# append to tail
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# a1 = value
# returns
# nothing
slist_append:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -8
sw ra, 0(sp)
# capacity check
lw t0, 0(a0) # t0 = len
lw t1, 4(a0) # t1 = max len
bge t0, t1, slist_append_capacity_check_fail
sw a0, 4(sp) # store slist
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of list
mv a2, a1 # a2 = value
mv a1, t0 # a1 = n (current len)
call set_nth
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = slist
lw t0, 0(a0) # t0 = len
addi t0, t0, 1
sw t0, 0(a0)
j slist_append_capacity_check_end
slist_append_capacity_check_fail:
# raise capacity warning
mv a1, a0
li a0, 4
ecall
slist_append_capacity_check_end:
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 8
ret
相对的,末尾删除的操作也同样十分简洁。在确保当前表非空后,减少一个表长即可(后续加值会覆盖此时未抹去的数据)。
# pop the tail
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# returns
# a0 = value of tail
slist_pop:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -4
sw ra, 0(sp)
# capacity check
lw a1, 0(a0) # t0 = len
beq a1, zero, slist_pop_capacity_check_end
addi a1, a1, -1
sw a1, 0(a0) # update len
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of list
call get_nth # a0 = value of tail
slist_pop_capacity_check_end:
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 4
ret
任意位置的插值/删除
由于顺序表各元素位置确定,而且通常要求插入后保序,所以我们一定需要做表内数据转移的操作。为此,insert需要先移后插,而remove则直接覆盖即可。
# insert to nth
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# a1 = n
# a2 = value
# returns
# nothing
slist_insert:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -20
sw ra, 0(sp)
# capacity check
blt a1, zero, slist_insert_capacity_check_fail
lw t0, 0(a0) # t0 = len
blt t0, a1, slist_insert_capacity_check_fail
lw t1, 4(a0) # t1 = max len
bge t0, t1, slist_insert_capacity_check_fail
addi t1, t0, 1 # t1 = t0 + 1
sw t1, 0(a0) # update len
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of list
sw a0, 4(sp) # store addr of list
sw a2, 8(sp) # store the saving value
sw t0, 12(sp) # store the current index of loop
sw a1, 16(sp) # store the end index of loop (AKA n)
slist_insert_transfer_loop_start:
lw a1, 12(sp) # a1 = current idx
lw t0, 16(sp) # t0 = end idx
bge t0, a1, slist_insert_transfer_loop_end # idx <= end
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = addr of list
addi a1, a1, -1
call get_nth # a0 = [current idx - 1]
mv a2, a0 # a2 = [current idx - 1]
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = addr of list
lw a1, 12(sp) # a1 = current idx
call set_nth # [current idx] = [current idx - 1]
lw t0, 12(sp) # t0 = current idx
addi t0, t0, -1
sw t0, 12(sp) # update current idx
j slist_insert_transfer_loop_start
slist_insert_transfer_loop_end:
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = addr of list
lw a1, 16(sp) # a1 = n
lw a2, 8(sp) # a2 = the saving value
call set_nth
j slist_insert_capacity_check_end
slist_insert_capacity_check_fail:
# raise capacity warning
mv a1, a0
li a0, 4
ecall
slist_insert_capacity_check_end:
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 20
ret
代码量虽然稍多,但实际做的事情却十分纯粹。用C语言改写的话大致如下。
void insert(Slist* slist, int n, int value) {
for (int idx = slist->idx; idx > n; --idx)
slist->array[idx] = slist->array[idx - 1];
slist->array[n] = value;
}
同样remove可如下实现,思路与insert大体相同。
# remove the nth item
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# a1 = n
# returns
# nothing
slist_remove:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -16
sw ra, 0(sp)
# capacity check
blt a1, zero, slist_remove_capacity_check_fail
lw t1, 0(a0) # t1 = len
bge a1, t1, slist_remove_capacity_check_fail
addi t0, t1, -1 # t0 = len - 1
sw t0, 0(a0) # update len
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of list
sw a0, 4(sp) # store addr of list
sw a1, 8(sp) # store the current index of loop
sw t0, 12(sp) # store the end index of loop
slist_remove_transfer_loop_start:
lw a1, 8(sp) # a1 = current idx
lw t1, 12(sp) # t1 = end idx
bge a1, t1, slist_remove_transfer_loop_end
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = addr of list
addi a1, a1, 1 # a1 = current idx + 1
call get_nth # a0 = [current idx + 1]
mv a2, a0 # a2 = [current idx + 1]
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = addr of list
lw a1, 8(sp) # a1 = current idx
call set_nth # [current idx] = [current idx + 1]
lw t0, 8(sp) # t0 = current idx
addi t0, t0, 1
sw t0, 8(sp) # update current idx
j slist_remove_transfer_loop_start
slist_remove_transfer_loop_end:
j slist_remove_capacity_check_end
slist_remove_capacity_check_fail:
# raise capacity warning
mv a1, a0
li a0, 4
ecall
slist_remove_capacity_check_end:
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 16
ret
由于每次操作都至多会移动表中$n$个元素,所以时间复杂度为$O(n)$。
指定元素查找
对于查找操作,我们只需要在维护一个当前下标的同时对整个表进行遍历比较,比对成功后直接返回当前的下标即可。因为至多遍历$n$个元素,所以查找操作的时间复杂度也为$O(n)$。具体实现如下。
# find the given value
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# a1 = value
# returns
# a0 = index
slist_find:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -20
sw ra, 0(sp)
lw t0, 0(a0) # t0 = len
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of list
sw a0, 4(sp) # store addr of list
sw zero, 8(sp) # store the current idx of loop
sw t0, 12(sp) # store the end idx of loop
sw a1, 16(sp) # store the finding value
slist_find_loop_start:
lw a1, 8(sp) # a1 = current idx
lw t0, 12(sp) # t0 = end idx
bge a1, t0, slist_find_loop_end
lw a0, 4(sp) # a0 = addr of list
call get_nth # a0 = [current idx]
lw t0, 16(sp) # t0 = the finding value
beq a0, t0, slist_find_loop_end
lw t0, 8(sp) # t0 = current idx
addi t0, t0, 1
sw t0, 8(sp) # update current idx
j slist_find_loop_start
slist_find_loop_end:
# result check
lw a0, 8(sp) # a0 = current idx
lw t0, 12(sp) # t0 = end idx
blt a0, t0, slist_find_result_check_end
li a0, -1
slist_find_result_check_end:
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 20
ret
在整个操作的最后我们需要检查当前下标的具体数值,如果已经越界则说明已经遍历了所有元素却仍没比对成功,对于此种情况我们可返回$-1$以示区分(虽然直接返回越界下标值也可)。
高阶函数
对于一些复杂的可迭代对象的操作我们常常会用到一些高阶函数辅助,比如:map和filter等等。在C语言中函数可以以函数指针的方式进行传递,在汇编里我们则可以通过伪指令la获取该函数标签的地址,然后使用jalr指令直接进行跳转。
对于映射操作,我们一般只需要两个参数:映射函数和可迭代对象,并返回一个新的同类迭代对象。这里为了增强使用灵活性,我们为它新增一个原地置换选项。具体实现如下。
# map
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# a1 = function for mapping
# a2 = in place option (0 for false)
# returns
# a0 = address of mapped slist
slist_map:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -24
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw a1, 4(sp) # store map func
sw a0, 8(sp) # store address of src slist
# prepare dst slist
bne a2, zero, slist_map_inplace_check_end
lw a0, 4(a0) # a0 = max len
call make_slist # a0 = addr of dst slist
slist_map_inplace_check_end:
sw a0, 12(sp) # store address of dst slist
lw t0, 8(sp) # t0 = addr of src slist
lw t0, 0(t0) # t0 = len of src slist
sw t0, 0(a0) # set len of dst slist
sw zero, 16(sp) # store the current idx of loop
sw t0, 20(sp) # store the end idx of loop
slist_map_loop_start:
lw a1, 16(sp) # a1 = current idx
lw t0, 20(sp) # t0 = end idx
bge a1, t0, slist_map_loop_end
lw a0, 8(sp) # a0 = addr of src slist
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of src list
call get_nth # a0 = src[current idx]
lw t0, 4(sp) # t0 = map func
jalr t0 # a0 = func(src[current idx])
mv a2, a0 # a2 = func(src[current idx])
lw a0, 12(sp) # a0 = addr of dst slist
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of dst list
lw a1, 16(sp) # a1 = current idx
call set_nth # dst[current idx] = func(src[current idx])
lw t0, 16(sp) # t0 = current idx
addi t0, t0, 1
sw t0, 16(sp) # update current idx
j slist_map_loop_start
slist_map_loop_end:
lw a0, 12(sp) # a0 = addr of dst slist
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 24
ret
然而对于筛选操作,原地置换则会引起一些不必要的复杂性,所以我们只实现返回新对象的效果。
# filter
# parameters
# a0 = address of slist
# a1 = function for filtering
# returns
# a0 = address of filtered slist
slist_filter:
# deepen stack
addi sp, sp, -28
sw ra, 0(sp)
sw a1, 4(sp) # store filter func
sw a0, 8(sp) # store address of src slist
# prepare dst slist
lw a0, 4(a0) # a0 = max len
call make_slist # a0 = addr of dst slist
sw a0, 12(sp) # store address of dst slist
sw zero, 16(sp) # store the current idx of loop
lw t0, 8(sp) # t0 = addr of src slist
lw t0, 0(t0) # t0 = len of src slist
sw t0, 20(sp) # store the end idx of loop
slist_filter_loop_start:
lw a1, 16(sp) # a1 = current idx
lw t0, 20(sp) # t0 = end idx
bge a1, t0, slist_filter_loop_end
lw a0, 8(sp) # a0 = addr of src slist
lw a0, 8(a0) # a0 = addr of src list
call get_nth # a0 = src[current idx]
sw a0, 24(sp) # store src[current idx]
lw t0, 4(sp) # t0 = filter func
jalr t0 # a0 = func(src[current idx])
beq a0, zero, slist_filter_check_end
lw a0, 12(sp) # a0 = addr of dst slist
lw a1, 24(sp) # a1 = src[current idx]
call slist_append
slist_filter_check_end:
lw t0, 16(sp) # t0 = current idx
addi t0, t0, 1
sw t0, 16(sp) # update current idx
j slist_filter_loop_start
slist_filter_loop_end:
lw a0, 12(sp) # a0 = addr of dst slist
# restore stack
lw ra, 0(sp)
addi sp, sp, 28
ret
测试
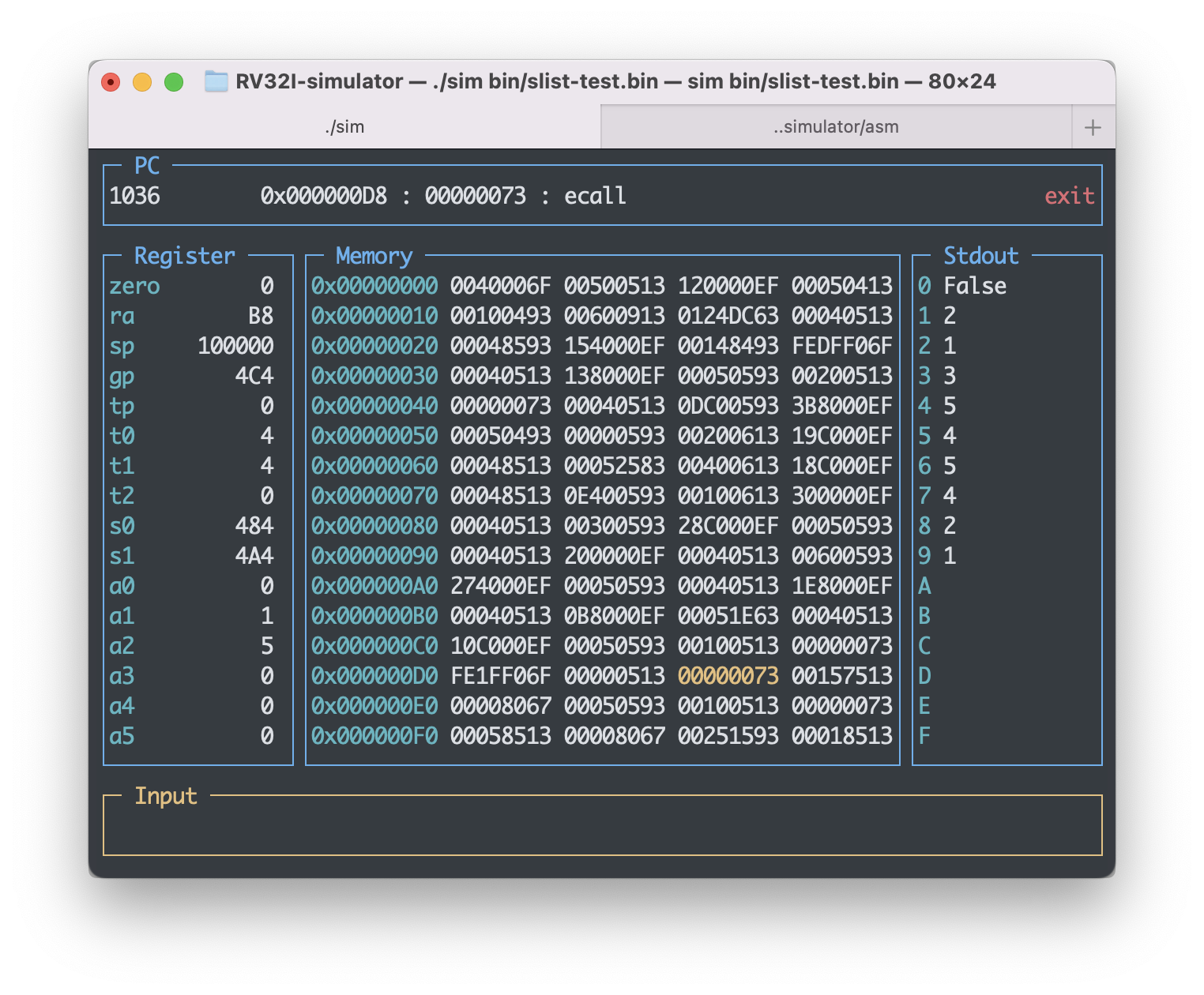
为了涵盖所有的操作,在开发的过程中我以如下流程进行了测试。
因此运行代码后我们将在数出框内看到,三次标星号位置的输出。第一次为非空(False),第二次应为2, 1, 3, 5, 4,第三次将会是5, 4, 2, 1。在第三次输出前,由于6不在表中,所以我们会看到一次删除不存在下标内容导致的容量警告(capacity warning)。最终效果如下图。